
In general, it is a good idea to use Fresnel for every material you create. To imitate this effect in Vray, you can use the Fresnel Reflections option. If you look directly at something (90°), the reflection is much weaker than if you look at it with a small angle. The smaller the viewing angle, the stronger the reflection. Notice how the reflection gets stronger as the floor goes further from the camera (or the closer it approaches the edge of the bowling ball). Even when some materials initially appear to be non-reflective, they will reflect quite a bit when they nearly parallel to the direction you’re looking at. In general, the lower the angle, the stronger the reflection becomes. Real world objects have different strengths of reflections, depending on the viewing angle relative to your line of sight.
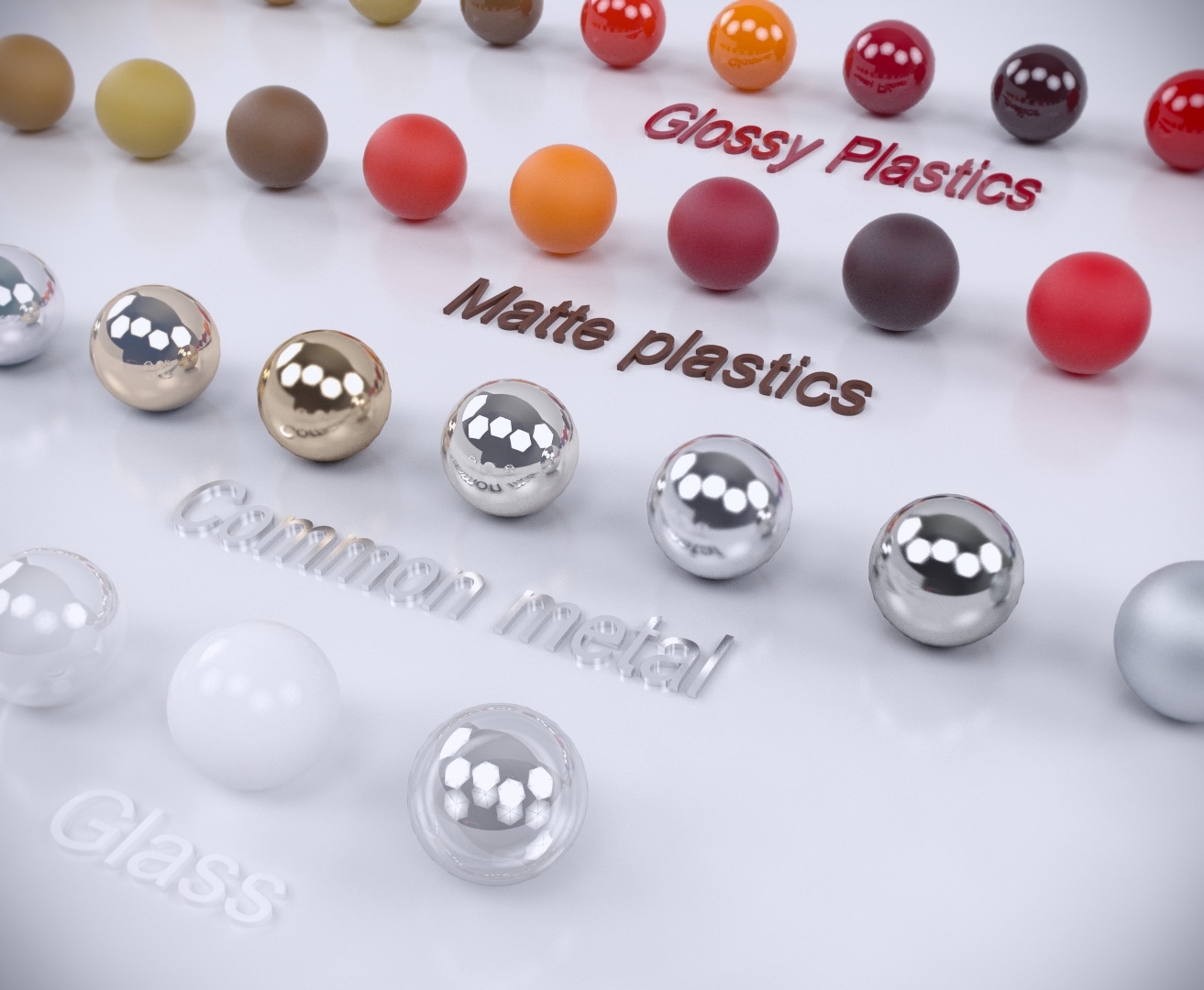

The problem is that the light reflects equally at all angles. So, why does our material look so artificial? In general, it may be best to keep the Reflection value in the range from 1~230 for realistic results. Also, it’s best to use a Map or a Texture instead of a simple color. The same principle of Diffuse map applies– if it’s not a shiny, slick studio render, there are bound to be some imperfections in the reflection amount. The Reflections (just like most other maps in V-Ray) can be defined by using a color, a map, or a texture. (It’s not entirely as simple as that, but that’s the general idea on how Diffuse and Reflection interact.) Drop it down to pure black and only the Diffuse is visible. Use a darker color and the Diffuse will start to show through. At 100% strength, it shows pure reflection of the environment, lights, etc. Perhaps it can be easier to understand how the Reflection works if you imagine it as a layer on top of the Diffuse. It also features a lot more options than Diffuse. This week, we’ll be moving on to: ReflectionĪfter Diffuse, Reflection is the second most important component of the VrayMtl.

Last week, we talked about the Diffuse tab. The information covered here is generally useful in V-Ray for C4D, but the specific fields and values may be different. While the example images are from 3ds Max, the same concepts and settings can be used in V-Ray for Maya.

We’ll cover the theory behind many of the features of the material and give you specific examples of settings and tricks to use.
#Vray materials series#
It's only used in the shading of Metaballs surfaces defined by the particles. It can be added to any Particle Flow event.In this series of Turbo Tips, we’re giving you an in-depth guide to regular V-Ray Material. VRayParticleColor – It is an operator that creates additional color information for particles. vrmat files which can be loaded using the VRayVRmatMtl material. vrmat converter can be used to convert materials in 3ds Max to. Thus instead of just being in a positive or negative direction, displacement can occur in many combined directions. Vector displacement, unlike standard displacement which displaces only in a positive or negative direction from the surface of the low poly base, allows displacement to occur in all 3 axes. You can then generate a map that when used with vector displacement turns the base geometry into the target geometry. It requires that you have a low poly base geometry and a high poly target geometry.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
